- PO Box 989 Mullumbimby Contact us
- Call Us: +61 2 6684 3173
Basalt Fibre
Basalt is an igneous volcanic rock formed by the melt from the earth's mantle when it decompresses. It contains huge crystals in a fine quartz-like complex ball. Basalt fibers are used to create alternative building materials to contemporary metal props; the likes of steel and aluminum. After basalt stone has been extruded, it is taken through a process of conversion to wool that resembles metals which is an ensemble of pyroxene, olivine and plagioclase materials. Basalt mesh is used in frameworks of Eco Built system panels to reinforce our structures owing to their superior structural integrity.
A Little Bit More On Basalt Fiber
Compared to the ubiquitous carbon and glass fibers, basalt fibers emerge top with magnificent technical characteristics, superior performance and unbeatable cost effectiveness. Basalt fibers spring from a raw material of volcanic origin which are melted at temperatures as high as one thousand four hundred degrees Celsius. The mass of molten basalt fibers is passed through a platinum bushing which extends them into longer strands. Basalt mesh and rebar are then formed once these fibers are woven through a pultrusion.
Advantages of Basalt Fiber
The chemical resistance of basalt fiber is so high that it is impassive even to strong concentrated acidic solutions. It exhibits very high thermo-stability as a result of its high thermal resistance. Moreover, it also has low flammability. It is mechanically strong, resistant to abrasion and readily elastic. It does not degrade easily even when subjected to extreme temperatures even as high as nine hundred degrees Fahrenheit. What's more, its tensile strength is superior to that of a steel mesh of equal size. Basalt fiber also exhibits high thermal and acoustic insulation properties. Basalt fiber also has high electrical insulating properties. On an environmental front, basalt fiber is a renewable alternative to metal building materials. It is also ecologically clean and non-toxic to the end user.

Download the Sustainable Domes Walkthrough app now - just like our facebook page and look for the details.
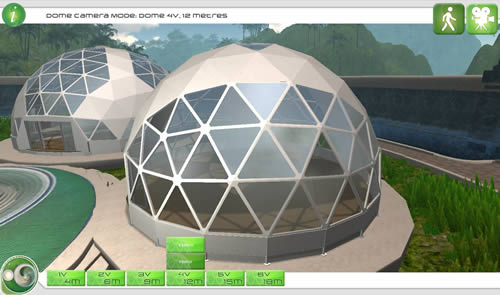
15m Residential Dome

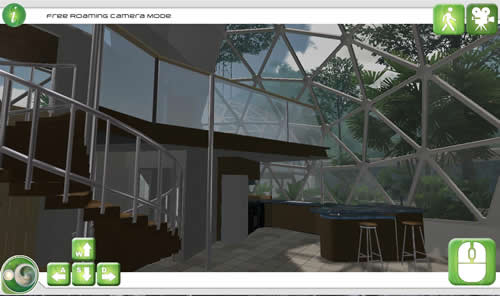
15m Residential Dome Internal
12m and 15m Residential Domes