- PO Box 989 Mullumbimby Contact us
- Call Us: +61 2 6684 3173
FAQs About Geodesic Domes
Geodesic domes have drawn several questions over the years. The public got a glimpse of the first geodesic dome in 1926. It was designed by Walther Baursfeld who was then a chief engineer at Carl Zeiss optical company. It was not made for the fanciest of reasons- it was a simple storage for his planetarium projector. Two decades passed before geodesic domes were reintroduced to the world by Robert Buckminister Fuller (Bucky). This eccentric man who got expelled twice from Harvard University helped to popularize geodesic domes and it caught on. The following are answers to some of the FAQs about geodesic domes.
What Is A Geodesic Dome?
A geodesic dome is a spherical or semi-spherical structure whose outer shell is composed of several circles which intersect to form triangles. Basically, they look like soccer balls or half spheres with several triangular supports. Examples of world famous geodesic domes include The Montreal Biosphere (The Biosphere), The Telus World of Science, Spaceship Earth (the name coined by Bucky) at Epcot in Disneyland and the Tacoma Dome.
What Makes Geodesic Domes Strong?
Geodesic domes are reputed for their extraordinary strength. The network of interlocking triangular elements in their framework ensure that weight loads are distributed evenly across the entire structure as opposed to conventional structures where weight loads are distributed at ninety degrees. This gifts geodesic domes tremendous strength despite their lightness of the materials that make them up. Moreover, this strength makes them to be self supporting. This means that they do not require structural supports such as supporting beams to hold them up.
Are Geodesic Domes Expensive?
Given their aesthetic appeal and futuristic design, you would be forgiven to think that geodesic domes are expensive. The truth of the matter is that geodesic domes are considerably more affordable compared to conventional building structures. The materials used in constructing geodesic domes are cheaper compared to those used in constructing conventional houses. Moreover, the ease of assembly and disassembly of geodesic domes mean that the labor hours required to set up one is reduced thus resulting in cheaper manpower. Lastly, once set up, geodesic domes require very little maintenance costs thus reducing the cumulative long term costs of owning a geodesic dome. Geodesic domes are therefore less costly than conventional buildings.
Why Do People Consider Geodesic Domes To Be Sustainable?
You have probably stumbled upon text referring to geodesic domes as sustainable. In the wake of climate change and other environmental concerns, more emphasis is placed on sustainability. It is no surprise therefore the sustainability qualities of geodesic domes are being mentioned regularly. Geodesic domes are considered sustainable because of their high energy efficiency, the fact that they are toxic free, the nature of their materials and their resistance to natural disasters.
Can Geodesic Domes Withstand Natural Calamities?
The triangular elements of geodesic domes offer them high structural integrity and strength. Their design also makes them aerodynamic. They are also devoid of roof structures. All these make geodesic domes to be a fortress in instances of natural calamities such as storms and earthquakes.
Can I Build My Own Geodesic Dome?
Geodesic domes are easy to build from scratch provided you have the right materials and the willingness to follow instruction. You can also opt to assemble SIPs distributed by manufacturers of geodesic domes. The other option is to outsource the entire geodesic building process to a company such as Sustainable Domes.
Download the Sustainable Domes Walkthrough app now - just like our facebook page and look for the details.
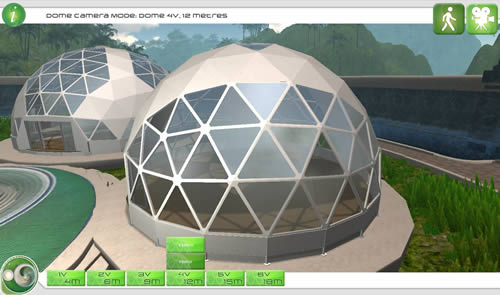
15m Residential Dome

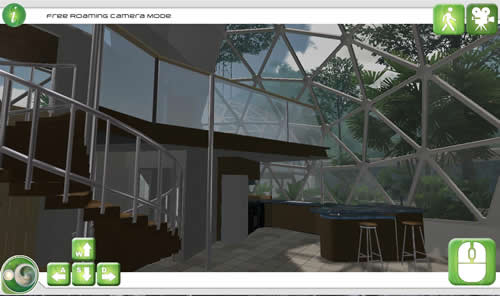
15m Residential Dome Internal
12m and 15m Residential Domes